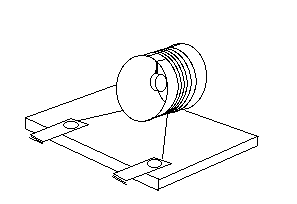
An ammeter is made by hanging a magnet from a string inside a tube around which is wrapped a coil of wire carrying an unknown current.
Build your own ammeter and use it to detect electric current
Introduction
An ammeter is a device that detects an electric current. With some readily available materials, you can build your own ammeter and use it to measure current produced by batteries including homemade batteries and generators.
Material

Assembly
Cut a 2 cm length from the tube.
Wind a coil of at least 100 turns of magnet wire around the
section of tube.
Leave at least 10 cm of wire free at each end of the coil.
Use masking tape or hot melt glue to hold the coil in place on its
tube.
Hot melt glue the tube to the wood base.
Sandpaper the ends of the magnetic wire to remove the insulating
layer of enamel. The ends of the wire should appear as shiny
copper.
Take one free end of the wire from the coil. Fold the aluminum foil
into two rectangles, several layers thick and about 1 cm x 2.5 cm.
Slip the bare copper end of the wire into the aluminum foil and fold
the foil over several times. Use a pushpin to mount the aluminum foil
to the wood base. Do the same with the other free end of the wire.
Mark a + sign near one end of the wire, it does not matter which
end.
Hang the magnet from a string in the center of the coil: tie a thread around the sides of the button magnet and secure it with very small pieces of masking tape. Make a slit in the center of the top of the tube, run the slit up to the edge of the coil. Make another slit about 1 cm away. Hang the magnet by slipping its thread through the first slit then slip the thread through the second one. The friction of the thread going through two slits will hold the magnet in place. Adjust the thread so that the magnet hangs in the middle of the coil
To do and notice
The hanging magnet aligns itself with the earth's
magnetic field, just like a compass needle. (see the activity titled,
"Where's
North?")
To use the ammeter, turn the coil so that the coil is lined up north
and south. When you look in the end of the tube you should see the
edge of the magnet.
Attach the battery to the leads. Attach the + side of the battery to
the + lead of the meter. The hanging magnet should turn so that one
face is toward the meter leads. Attach a piece of tape to that face
and print + on the tape.
Reverse the connections to the battery the magnet should rotate the
opposite direction.
Your ammeter is very sensitive. The magnets in ours deflect 45 degrees when 10 milliamps flow through them. To measure the sensitivity of your meter connect a calibrated ammeter in series with a battery and a variable resistor. Change the resistance until the ammeter magnet turns 45 degrees read the current on the calibrated ammeter
You can use your ammeter to measure the current produced by your own lemon batteries or homemade generators.
What's Going On?
The electric current running through the coil of wire produces a magnetic field, which pushes on the the hanging magnet, making it twist. The hanging magnet is held in its no-current position by the earth’s magnetic field. The stronger the current in your coil, the stronger the magnetic field produced by the coil and the more the magnet twists.
|
Scientific Explorations with Paul Doherty |
|
2 August 2000 |